
The impact of temperature on the range of different Electric cars brands and models is, for the most part, the same. But what is the best temperature for electric car range?
The driving range of an electric car is negatively impacted by both cold and heat. The worst is when it’s cold. When it comes to driving range, 21.5 celsius is the ideal temperature for electric vehicles.
An analysis done by researchers determine whether all-electric car models were equally impacted by temperature and how it affects range.
In order to determine this, Geotab examined anonymized data from 5.2 million journeys made by 4,200 electric cars representing 102 distinct make/model/year combinations. They next looked at average vehicle trip efficiency by temperature.
Its analysis shows that:
- The majority of electric cars have a similar temperature range curve, which was unaffected by brand or model.
- Both cold and hot conditions have an effect on range, although colder climates have a bigger impact.
- The ideal temperature for a vehicle trip is 70F (21.5C).
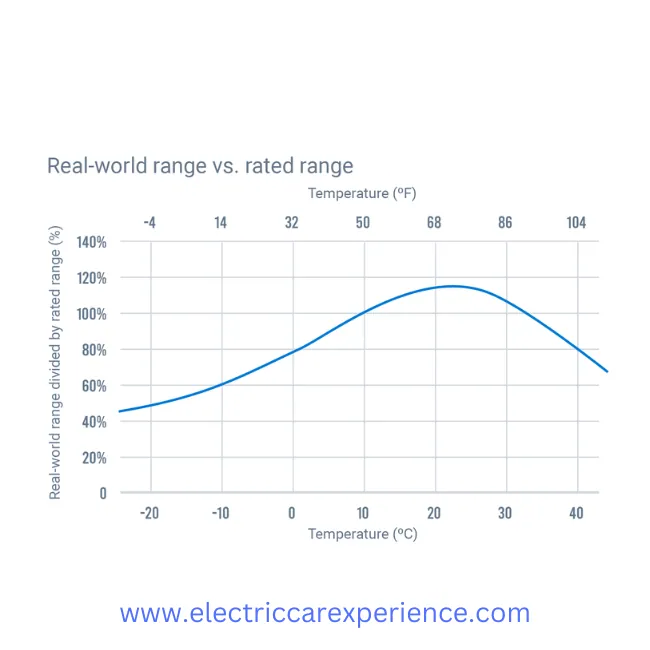
As earth’s climate rarely reaches temperatures above 122F (50C), we don’t know (and, ideally, don’t need to care) what happens to our range beyond that threshold. As a result, the real-world impact is less noticeable at hot temperatures.
[toc]
Why Temperature Affects Your Electric Car
Your Electric car’s battery most likely contains lithium, a material susceptible to high temperatures. The electrolyte fluid in the battery will be thicker in colder weather, making it more challenging to store and transport energy.
The worst offender among them all, though, is not your battery’s ability to function in hot and cold environments. The heating system in your car is the biggest offender.
In order for the battery to operate at its optimum, electric cars are made to heat or cool the battery. Additionally, a portion of the energy is consumed to meet this requirement because the ideal temperature for most batteries is between 15 and 30 degrees Celsius.
The heating system of the car affects air conditioning as well.
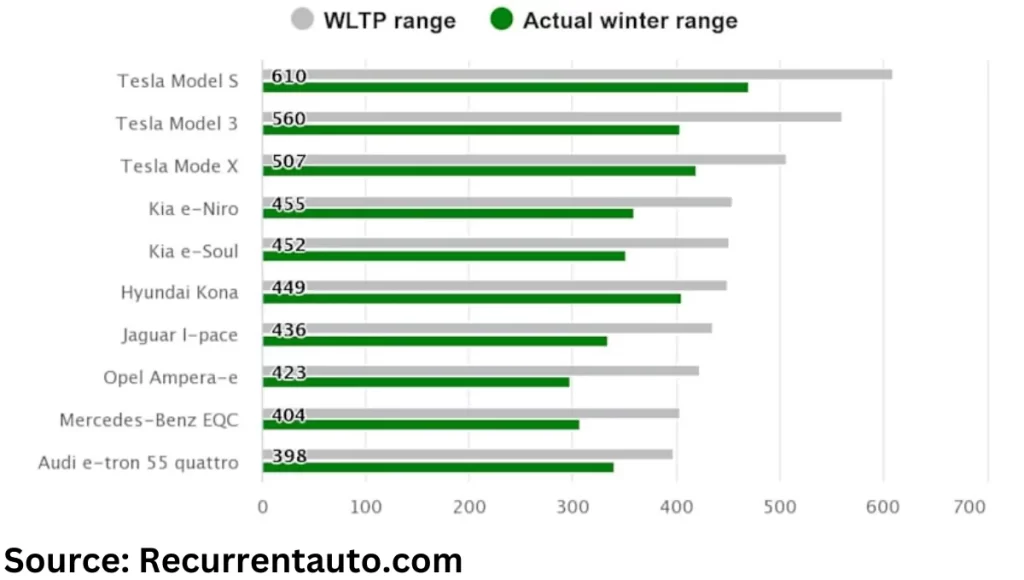
A hot summer day makes you want cooler air in the cabin, whereas driving in – 20 degrees makes you more likely to crank up the heat. Regardless of whether the option is chosen, the end result is the same: the energy is utilized to regulate the air temperature within the car rather than to move it.
Tips to Increase The Range of Your Electric Car
Here are two tips that will help you rack up a few additional kilometers on the road if you want to increase your electric car’s range in all types of weather:
Instead of using the standard heating system, turn on the seat and steering wheel heater. Compared to the heating system’s 300–5000 Watts of power, the seat and steering wheel heater utilizes only 75 Watts.
Before you start driving, preheat the vehicle. The automobile uses less energy from the battery when the heating system is turned on while it is still plugged into your charging station.
Why Do Lithium-ion Batteries Have Cold Sensitivity?
In particular, conductivity and diffusivity are slowed down by cold weather, which has the following effects:
Increased Charging Time (Increased Impedance)
Range capacity is temporarily reduced, mostly because of the heating system. The use of climate control may deplete the primary battery’s charge as the power to heat and cool your automobile comes from the same battery that powers it.
Your battery should be above freezing before charging, despite the fact that cold-related range effects are transient. In most automobiles, the battery management system (BMS) has some kind of temperature control that will halt high voltage or speedy charging if the battery is too cold.
Energy will often be used to maintain a comfortable temperature if your car is on or plugged in. The two exceptions to this rule are Tesla, which will activate thermal management even if the car is not plugged in or running, and Nissan Leaf, which only has thermal regulation turned on when the temperature drops below -20C (-4F).
Lithium Plating is The Science of Charging in Cold Temperatures.
Please take note that the next section explains the physical phenomena that researchers have found in specific lithium-ion batteries. Modern electric vehicles contain battery management technologies that should shield your battery from this kind of long-term deterioration.
If the battery is below freezing point
When your battery is below freezing, stay away from supercharging or high-voltage charging. Using the in-car navigation system to find a charger is another common way to prepare your battery for charging.
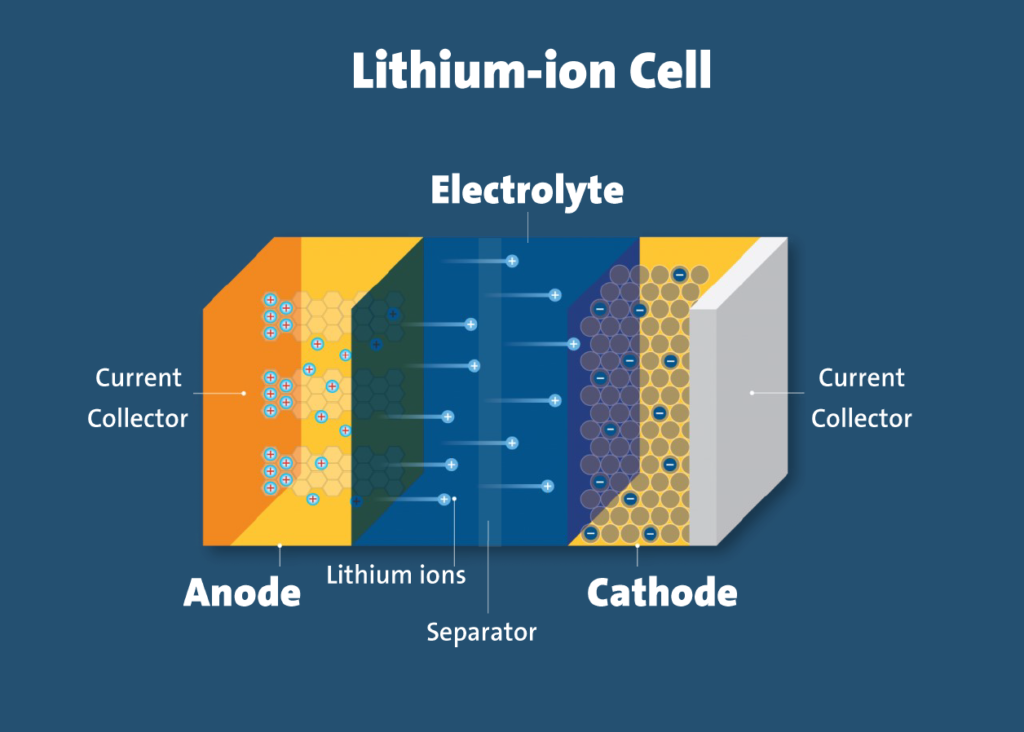
A metallic buildup known as lithium plating occurs at the negative battery node (the anode, where the energy goes during charging). In other words, as ions move through battery cells more slowly in colder temperatures, lithium builds up outside the node and transforms into an inert metal.
This metal obstructs future energy flow and consumes some of the lithium that should be powering the battery. This could result in a reduction in power and range for single-cell observations.
Battery Anode and Cathode Flow
If you’re curious about a little additional information, battery anodes are made of substances with lattice-like structures, such as graphite. Because lithium ions flow from the cathode to the anode and are stored in this grid-like structure, this is significant because it helps batteries charge. Intercalation is the name given to this process.
The ions must be pushed into the anode and lodged in the grid using force (in this example, current). The ions enter the anode more slowly if this process takes place when it is cold outside, and the accumulation of lithium outside may result in the formation of metallic plating. While some of these ions eventually pass through the anode and reduce capacity and increase internal battery resistance, others remain plated outside.
Keep in mind that your car’s computer systems should warm up your battery first and sluggishly charge it till it is secure to do so. On the other hand, a lithium-ion battery that has previously been charged can be used without concern at extremely cold temperatures. Since the cold temperature reduces ion flow, you’ll notice a temporary reduction in range, but there won’t likely be any long-term harm.
What Occurs When I Charge My Electric Car in the Heat?
During charging, high temperatures can harm batteries. High temperatures make the electric current that moves lithium ions from one node of the battery to the next more powerful, which puts the receiving end under physical strain and damage.
The battery node gets increased stress fractures and damage as the temperature or current increases. All of these tiny fissures and cracks serve as secondary reaction surfaces, depleting the lithium supply and producing chemicals that obstruct the free flow of energy.
For those who are interested, we can once more become a little more technical.
Intercalation Process
The intercalation process, which was previously explained, is required for a lithium-ion battery to function but puts the anode under physical strain. Higher charging temperatures cause the lithium ions to intercalate more aggressively, which frequently results in minute fissures and cracks.
In particular, new sites for further SEI development are created, creating new surfaces for chemical interactions between the anode and the available lithium. Any more reactions exhaust lithium and cause capacity to wane.
Furthermore, if all the ions are unable to be stored within the anode grid, they may become trapped outside the anode and conduct chemical processes that result in the formation of inert materials, such as lithium plating.
Both of these factors have the potential to raise the battery’s internal resistance and decrease the amount of power it can hold.
On Hot and Cold Days, Some Advice for Extending Your Electric Car’s Range
As said, the auxiliary load is the main culprit for range loss in cold and hot climates. Therefore, reducing auxiliary load will contribute to increasing those miles:
Utilize the heated steering wheel and seats.
In comparison to heating your seat and steering wheel, which uses only 75 watts and conducts heat to your body by conduction, heating the cabin air requires 3000-5000 watts and is significantly less effective.
You won’t need to use the cabin heater if you make use of these increasingly popular features. However, in extremely cold weather, reducing cabin heating can only go so far, and your battery thermal management system will still waste energy.
Pre-Condition Your Car
Warm up before a long journey just like you would before exercising! Cool off if it’s too hot. By warming (or cooling) your car before you leave on your vacation, you can reduce the auxiliary demand by turning on the heaters while your car is still plugged in.
Profit from the guilt-free conditioning that electric cars enable. If you have the choice, you can achieve a comparable result by parking in a heated garage.
When It’s Really Chilly Or Hot Outside, Keep Your Car Plugged In.
Along with the advantages of preconditioning before a trip, automakers advise charging Cars when they are not in use on extremely hot or cold days. (Note: Active charging, which is preferable to avoid under extreme circumstances, especially heat, is not the same as passive charging.) When a car is plugged in, the internal system can maintain battery temperature regulation, thus extending the battery’s lifespan.
Drive Conservatively
The way you drive your electric car has an impact on your mileage range regardless of the weather. Energy is lost during rapid acceleration, braking, and high-speed driving. And doing so will keep you and your passengers safer, especially in icy conditions, and improve your mileage range.
You can use your electric car’s regenerative braking technology to recover energy and store it back in the battery by anticipating the need to brake and avoiding hard braking. The only thing to keep in mind is that the regenerative braking system will be less effective in freezing temperatures because cold batteries can’t absorb as much energy as warm ones.
Use The Eco Mode
Every electric car’s eco mode serves a somewhat different purpose, but generally speaking, they all waim to reduce power consumption and improve mileage by cutting back on the energy supply to the drive motor and high-energy functions like cabin heaters. Eco settings might actually make driving in the winter months safer. Because the automobile accelerates more slowly with less power going to the motor, there is less chance of tire spin on icy or snowy roads.
Check Your Tire Pressure
As the temperature drops, the pressure in the tires decreases, increasing rolling resistance and reducing mileage. It’s a good idea to check your tire pressure once a month, but it’s especially important now that the seasons bring along significant changes in outdoor temperature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the influence of temperature on efficiency may be measured; at lower temperatures, you can anticipate a less efficient Car and a smaller range. The estimated impacts of temperature on the Car are displayed.
As you can see, a lower climate can significantly impact efficiency, especially when it gets close to freezing. You can manage your fleet and ensure that your electric Cars meet your specific requirements by being aware of how temperature affects them.
FAQs
What Temperature is Best for Tesla Batteries?
What is the ideal temperature for Tesla? around 68-75F The battery can only work at this temperature without any restrictions. Not too chilly to require a heater, and not too hot to require an air conditioner.
Does Temperature Have an Impact On Tesla Batteries?
Numerous technologies in your Tesla Car are intended to enhance your driving experience in cold weather. It’s typical to observe an increase in energy consumption during cold weather because automobiles need more energy to heat the batteries and cabin.
A Tesla Battery May Become Excessively Cold.
If the Battery is too cold, the amount of regenerative braking may be reduced. The Battery warms up and regeneration power rises as you keep driving (see Regenerative Braking).
What is Tesla’s Optimum Operating Temperature?
Avoid subjecting the Model 3 to temperatures over 60° C or below -30° C for longer than 24 hours at a time for improved long-term performance.
What Temperature is Safe for Batteries?
What should the temperature of my phone be? When your smartphone is charging, running programs, or just lying idle, the manufacturers advise keeping it between 0 and 35 degrees Celsius, or 32 to 95 degrees Fahrenheit.
What Environment is Ideal for electric cars?
First off, the lithium-ion battery in an electric car operates best between 15 and 35 degrees Celsius. The lithium ions slow down and are unable to produce as much power as usual at temperatures considerably lower than this.
Is Fast Charging Beneficial for electric cars?
Consequences Of Repeated Fast Charging. The battery chemistry has an impact on an electric car’s capacity to tolerate higher charge currents. Faster charging will accelerate the rate at which an electric car’s battery capacity will degrade, according to conventional thinking in the
Posts Related to Electric Cars and Batteries.
- Why Did My Model 3 Range Decrease?
- Electric Cars Eventually Have More Range 2024
- Electric Car And Tesla Range Loss in Traffic Jam
- 4680 Battery Tesla Range (Model S, Model X, Model Y, Model 3) -Real Testing Data – Complete Guide 2024
- What is the best temperature for Electric car range?
- why does tesla not add more batteries to increase its electric car range?
- Tesla Model 3 Range City Vs Highway – Real Testing Done
- How Accurate Are Electric Car Ranges (Tesla, Nexon, Nissan, and Chevy)
- Can Tesla Put More Batteries In The Front Trunk Of The Tesla Model S To Improve Range?
- Electric Car Battery Range Extender
- Top 5 Reasons Why Electric Car Range Reduce in Cold Weather
